|
Through the patients' sera tests, doctors can judge whether a patient is infected with Helicobacter Pylori, and ascertain whether his condition belongs to the high risk group.
To further explore the impact of Helicobacter Pylori on the epithelial cells of the stomach, the NTU team established a model whereby the cancerization process of the stomach is simulated. Furthermore, the team used the "proteomics analyses platform" provided by NTU's Center for Genomic Medicine to successfully identify many proteins related to the carcinogenic mechanism of Helicobacter Pylori. Their efforts not only conduces to the understanding of the causes of gastric cancer, but is also instrumental in improving the effects of medicines for the cure of gastric cancers.
By using proteomics approaches we are able to identify GroES, which is a special protein of Helicobacter Pylori. The evidence of the presence of GroES's antibodies are conducive to the diagnosis of gastric cancer. Methods of examination are illustrated in the diagram. From the patients' serum samples we can ascertain whether there is the presence of gastric cancer-related GroES antibodies.
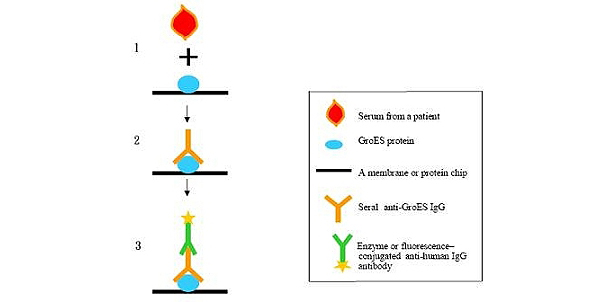
Detection of anti-GroES IgG from patients; sera is an indicator of the patient having gastric cancer. Patients with GroES deropositivity are recommended to accept invasive endoscpoy for early detection which will result in the increase of survival rate. One primary cause for the NTU research team's achievements has to do with the vast resources supplied by the NTU Center for Genomic Medicine. This center consists of 8 core laboratories, i.e., Proteomics and Protein Function Core Laboratory, Microbbial Genomics Core Laboratory, Biomedical Molecular Imaging Core Laboratory, Tissue Bank Core Laboratory, Transgenic Mouse Core Laboratory, Population Genetic Polymorphisms Core Laboratory, Bioinformatics and Biostatistics Core Laboratories, etc., lending state-of the art technological support to medical researches in various fields.
The Center places its research emphasis on two areas: death-causing cancers and infectious diseases for Taiwanese people. It aims to utilize new technology and new knowledge of medicine to understand the causes of diseases and the mutations of genes, thereby finding effective antigens and probing new methods of prognosis,developing pertinent vaccines and curative reagents, expanding medical application and facilitating bio-medical researches of all kinds.
|


