| |
 |
|
|
 |
| |
 |
|
|
:::
|
Convenor of the research team, Professor D. P. Tsai points out that, NTU's optical storage team based their research on the findings of the industry/academic cooperative plan sponsored by the National Science Council and the Ministry of Economic Affairs, and after receiving funding for the major equipments needed to conduct the research from the "En route to a top notch university" Project, the team was able to develop by leaps and bounds. They have been able to develop nano-analysis of near field optical disk, effectively narrowing the size of the record point to 90 nanometer (twenty times smaller than the smallest record point of current DVD's), thus greatly increasing optical density and recording capacity. So far the capacity of a single compact disc developed by the team is estimated to reach more than 150 GB, even up to 200 GB, which is 30 times the capacity of regular DVD discs.
The timely involvement from industry, government, and academic institutions with the research and development of nanotechnology creates a good opportunity for the optical storage industry of Taiwan to transform and upgrade, freeing itself from the oppression of heavy royalties, and becoming technologically independent. For the time being, the achievements made by the elites of NTU's nano optical storage research team are being actively integrated with the unique advantages of the existing domestic optical storage industry, and the results are expected to be very conducive to the creation of new products and increase of market value.
Excellence in Research (3)
New Knowledge and New Technology to Provide Cure to Hepatitis, Cancer and Infectious Disease Patients
|
NTU's Research Center for Medical Excellence has the most
important top talents and faculty in medical research (which include Dr, Ding shinn Chen,
Dr. Pan-Chyr Yang, and Dr. Pei-jer Chen, all three of them Academia Sinica academicians,
and over 27 members above doctoral level). Coupled with multifunctional core facilities
in genomics study, comprehensive teaching resources system and excellent graduate school
students, over the past few years the Center has outstanding research achievements in
the study of hepatitis, cancer, and infectious diseases and has an average of 40 articles
published in international medical journals every year. Related co-operations with the
industry, and patent applications have also been increasing year by year.
The following are the most recent achievements of the core laboratories of the Center:
|
The Microbial
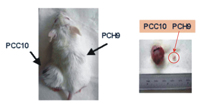
Genomics Core Laboratory of NTU has successfully established the mice mode
for continuous infection of chronic type B hepatitits. They discover that substantial
performance by HLJ1 genes can effectively inhibit tumor growth (pictured here
are photos showing the difference in tumor size)
|
|
Proteomics and Protein Function Core Laboratory:
To probe the impact of Helicobacter pylori on the human epithelial cells, NTU's Center for Genomic Medicine research team established the model system of Helicobacter pylori infection of human epithelial cells to simulate the cancerization process of the stomach. The use of "protein analysis platform" allowed the researchers to rapidly identify gastric cancer-related protein factors on a large scale, and the research results were published in the most representative journal on proteomics "Molecular and Cellular Proteomics." The research team now continues to conduct in-depth study of the gastric cancer –related protein factors in an effort to identify new targets for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Microbial Genomics Core Laboratory:
This core lab has successfully established the mice mode for continuous infection of chronic type B hepatitis. This new discovery is instrumental in the clarification of the pathogenic mechanism, and conduces to the development and evaluation of drugs and treatments.
Gene Microarray Core Laboratory:
The Gene Microarray Core Laboratory has recently discovered a new tumor suppressant gene related to lung cancer called HLJ1. This new found gene can inhibit the growth of lung cancer cells, while facilitating the regeneration and metastasis of blood vessels. Thus, HLJ1 has become a new standard for the treatment of lung cancer. In the meantime, the research team has found the gene factors of lung cancer, which allow doctors to predict the patients' survival rate, thus becoming an important reference for the personalized treatment of lung cancer.
The emphasis of the Research Center for Medical Excellence now centers on the most prevalent illnesses found among Taiwanese people such as "cancer" and "infectious diseases." The Center tries to utilize new knowledge and new technology in genomics medicine to solve the medical problems of Taiwanese nationals. The development strategy of the Center is to use the core lab of genomics medicine as the platform to continue the study of "cancer" and"infectious disease" while delving into other important areas such as neural science, high genetic diseases and stem cell studies. Future execution strategy involves exchange and cooperation with other related units within the university; actively bringing in fresh good blood from abroad,; developing international cooperation and academic exchanges on a large scale; continuing to introduce cutting-edge technology; etc., The purpose of all these, in sum, is to expand the medical research of NTU into the international arena in pursuit of excellence.
|
Copyright 2007 NTU Secretariat
|
|
Copyright © 2006 National Taiwan University
No. 1, Sec. 4, Roosevelt Road, Taipei, 10617 Taiwan(R.O.C.)
Phone: +886-2-3366-3366 Fax: +886-2-2362-7651
|